
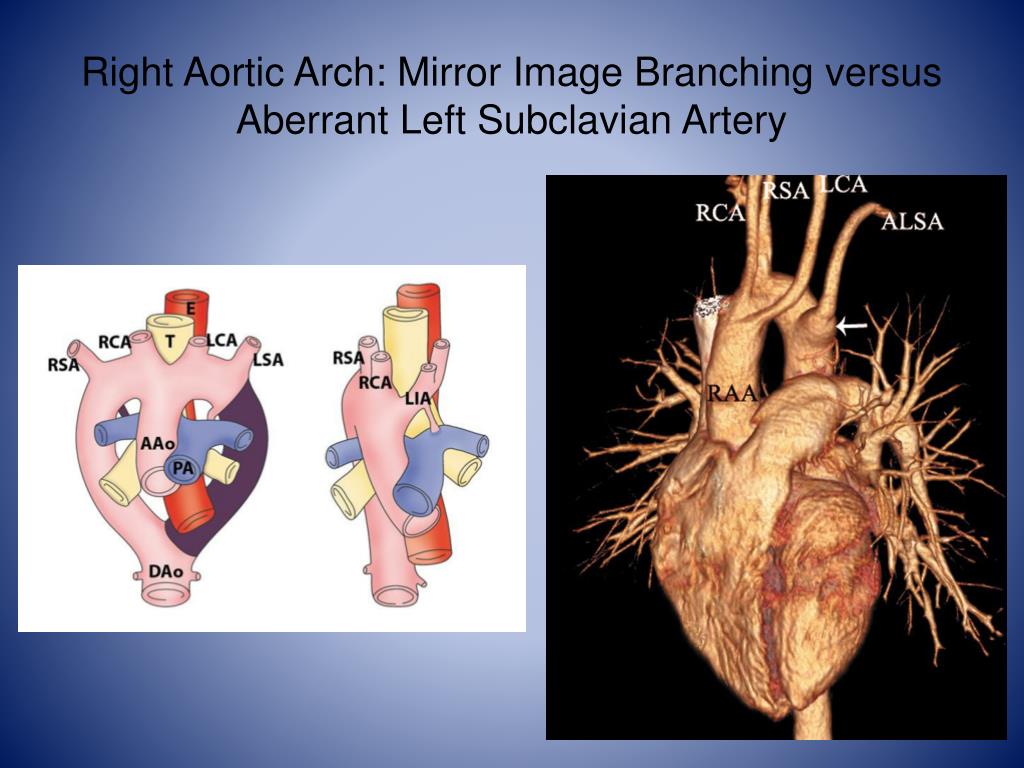
This has been observed in patients with single-ventricle anatomy. In nearly all patients the aortic arch sidedness is left, but rarely the IAA can be right sided with the descending aorta in the right hemithorax. In rare cases, when IAA is not associated with VSD, aortopulmonary window should be suspected. The VSD is typically conoventricular in origin and is associated with posterior malalignment of the conal septum and varying degrees of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (LVOTO) at the subvalvar and/or valvar level. Also seen are aortic valve anomalies, truncus arteriosus, and double-outlet right ventricle (RV). All patients have a patent ductus arteriosus, and most have a ventricular septal defect (VSD). Type B IAA is the most common (78%), followed by type A (20%) and type C (2%) ( Fig. Celoria and Patton 1 described the currently used anatomic definitions, in which type A is interrupted distal to the left subclavian artery (LSCA) type B is interrupted between the left subclavian and left carotid arteries in type B1 the origin of the right subclavian artery (RSCA) is on the descending thoracic aorta and type C is interrupted proximal to the left carotid artery. The incidence of IAA is 1% of all congenital heart defects. Interrupted aortic arch (IAA) is a rare but highly lethal form of congenital heart disease, carrying a mortality rate higher than 90% in the neonatal period if not treated. Huddleston MD, in Critical Heart Disease in Infants and Children (Third Edition), 2019 Classification and Anatomy Cytogenetic analysis using fluorescence in situ hybridization demonstrates deletion of a segment of chromosome 22q11, known as the DiGeorge critical region.Īndrew C. As one of the conotruncal malformations, an interrupted aortic arch, especially type B, can be associated with DiGeorge syndrome (cardiac defects, abnormal facies, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcemia). Patients with an interrupted aortic arch can be supported with prostaglandin E 1 to keep the ductus patent before surgical repair. When the ductus begins to close, severe congestive heart failure, lower-extremity hypoperfusion, anuria, and shock usually develop.

In newborns with an interrupted aortic arch, the ductus arteriosus provides the sole source of blood flow to the descending aorta, and differential oxygen saturations between the right arm (normal saturation) and the legs (decreased saturation) is noted. Interruption may occur at any level, although it is most often seen between the left subclavian artery and the insertion of the ductus arteriosus ( type A), followed in frequency by those between the left subclavian and left carotid arteries ( type B), or between the left carotid and brachiocephalic arteries ( type C). Coarctation of the aorta with transposition of the great arteries or single ventricle may be repaired alone or in combination with other corrective or palliative measures.Ĭomplete interruption of the aortic arch is the most severe form of coarctation and is usually associated with other intracardiac pathology.

Such patients usually have a long segment of narrow, transverse aortic arch in addition to an isolated coarctation at the site of the ductus arteriosus. The clinical manifestations depend on the effects of the associated malformations, as well as on the coarctation itself.Ĭoarctation of the aorta associated with severe mitral and aortic valve disease may have to be treated within the context of the hypoplastic left heart syndrome (see Chapter 458.10), even if the LV chamber is not severely hypoplastic.
Kliegman MD, in Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 2020 454.8 Coarctation With Other Cardiac Anomalies and Interrupted Aortic ArchĬoarctation often occurs in infancy in association with other major cardiovascular anomalies, including hypoplastic left heart, severe mitral or aortic valve disease, transposition of the great arteries, and variations of double-outlet or single ventricle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
